How to choose the correct hotend
Every machine has a characteristic tool and in the case of 3D printers is the hotend. It is responsible for melting the filament to be deposited in layers during the printing process.
Choosing a hotend is choosing between the time it will take to print, the surface quality, and the resistance of the piece.
With several models available it can be a complex task, but we have created this article with quality comparisons, time, and resistance to facilitate the task.

Content table:
- Time and resistance
- Superficial quality
- Hotends availability
Time and resistance
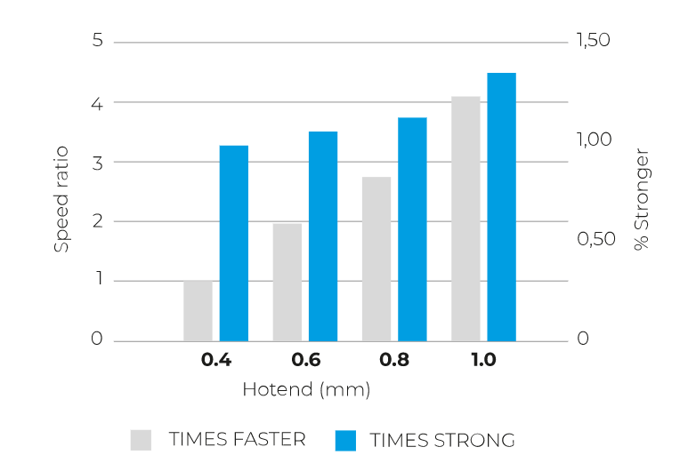
The amount of material that is extruded depends on the diameter of the hotend, the more quantity that can be extruded the less time the printing process will take. Also, the thickness of the layers determines how strong the part is.
|
The following graph shows how the resistance of the piece increases and the printing time is reduced as the diameter of the hotend increases.
|
 |
Superficial quality
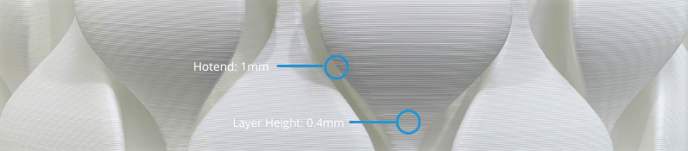
The layer height and the hotend thickness define the surface quality of the printed model. The surface becomes smoother when using thinner hotends and smaller layer heights.
The following images show how surface quality varies with different hotends and layer heights.


Hotends availability
Below you will find the list of hotends compatible with each printer:
 |
Hotends: 0.4mm / 0.6mm / 0.8mm / 1mm / X* /M* |
 |
Hotends: 0.4mm / 0.8mm |
|
|
Hotends: 0.4 / 0.6mm / 0.8mm / 1mm |
 |
Hotends: 0.4 / 0.6mm / 0.8mm / 1mm |
*The 0.6mm nozzle X hotend is only recommended for printing with fiber materials such as PAHT CF15 and PP GF30, for more information visit the following article: Hotend X - Fiber filled materials
*The 0.4mm nozzle M hotend is only recommended for printing with metal materials such as 316L and 17-4PH, for more information visit the following article: Hotend X - Fiber filled materials
|
You can help improve the BCN3D Knowledge Base. If you feel there are guides that we are missing or you found any error, please use this form to report it. Report form :) |